- English
- Español
- Português
- русский
- Français
- 日本語
- Deutsch
- tiếng Việt
- Italiano
- Nederlands
- ภาษาไทย
- Polski
- 한국어
- Svenska
- magyar
- Malay
- বাংলা ভাষার
- Dansk
- Suomi
- हिन्दी
- Pilipino
- Türkçe
- Gaeilge
- العربية
- Indonesia
- Norsk
- تمل
- český
- ελληνικά
- український
- Javanese
- فارسی
- தமிழ்
- తెలుగు
- नेपाली
- Burmese
- български
- ລາວ
- Latine
- Қазақша
- Euskal
- Azərbaycan
- Slovenský jazyk
- Македонски
- Lietuvos
- Eesti Keel
- Română
- Slovenski
- मराठी
- Srpski језик
중국 등방성 흑연 제조업체, 공급업체, 공장
Carbon/graphite material molding essentially involves increasing the density of the powder mixture and ensuring close contact between the aggregate and binder to produce a green body with a desired size, morphology, and minimal machining allowance. The four main molding methods are extrusion, compression molding, vibration molding, and isostatic pressing. Common carbon/graphite materials on the market (for example, charcoal used for household fires) are mostly formed using hot extrusion and compression molding (cold or hot). Isostatic pressing offers superior molding performance.
The principle of isostatic pressing is based on Pascal's law: pressure applied to a medium (liquid or gas) in a sealed container is uniformly distributed in all directions, with the pressure on the surface being proportional to the surface area. Isostatic pressing involves placing a sample, enclosed in a sealed container, within a high-pressure cylinder. Leveraging the incompressible nature of the liquid medium and its ability to uniformly transmit pressure, the sample is uniformly pressed from all directions. When the fluid is injected into the cylinder, the pressure is evenly transmitted in all directions according to the principles of fluid mechanics. The sample in the cylinder is then subjected to uniform pressure in all directions.
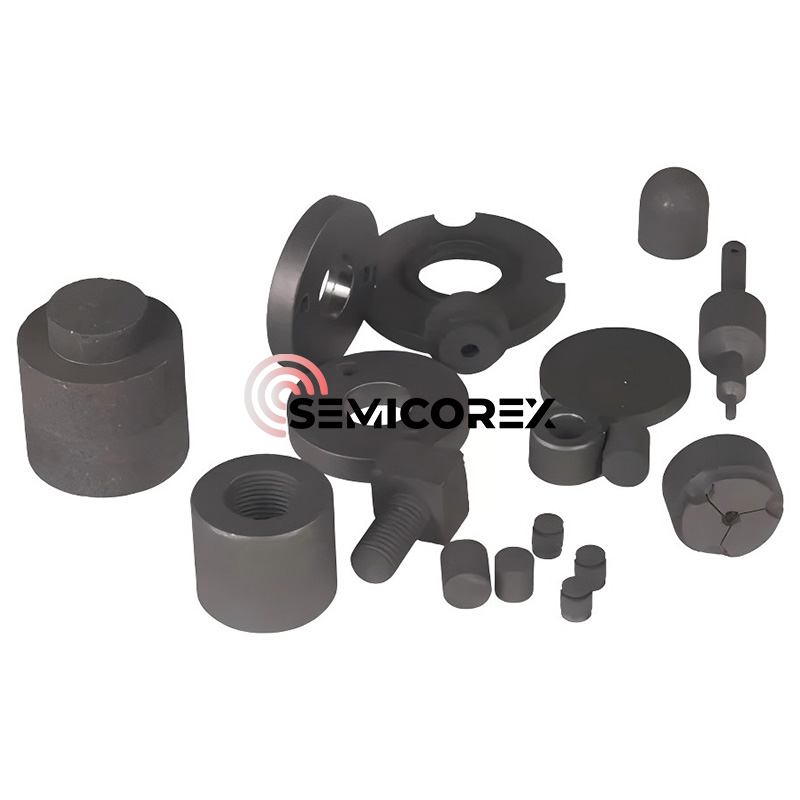
Due to the isostatic pressing method, isostatically pressed graphite exhibits excellent isotropy, with properties independent of shape, size, or sampling direction. The material possesses a dense microstructure, high mechanical strength, high surface hardness, and oxidation resistance. Strong performance and high-temperature resistance; the material has excellent thermal shock resistance and is less susceptible to cracking under rapid cooling and heating conditions.

1. Isotropy
Different molding methods result in different properties in different directions. This is primarily reflected in resistivity, thermal conductivity, mechanical properties, and thermal expansion coefficient. The general measurement method is to sample the product perpendicular to and horizontally from the pressure surface, measure the properties separately, and then divide the smallest value by the largest value to obtain the isotropy ratio.
Traditional carbon/graphite products exhibit significant anisotropy, i.e., the properties of the product are different in the directions perpendicular to and horizontal to the pressure surface. The corresponding difference in performance is generally greater than 1:1.1, hence the term anisotropy. In many cases, this difference is fully exploited, and the greater the difference, the better. Examples include graphite electrodes for steelmaking and brushes for motors. Many applications, such as EDM and single-crystal silicon thermal field applications, increasingly require carbon/graphite products to exhibit isotropy (with an orientation ratio within the 1:1.05 range).
2. Large Dimensions
The market is increasingly demanding larger product sizes. For example, single-crystal silicon products have grown from 6- and 8-inch sizes to 12-inch sizes. The size of graphite materials used in thermal fields is also increasing. This is also increasing. Similar trends are seen in other related industries. Graphite for EDM, continuous casting, and nuclear reactors also requires large-scale products. This is difficult to achieve using molding and extrusion methods. The primary problem with large-scale product production is calcination cracking, and the larger the product, the higher the chance of calcination cracking.
3. Fine Structure
As a structural material, it requires high physical and chemical properties. On the one hand, the finer the particle size of the carbon particles that make up the carbon/graphite material, the denser its texture and the higher its mechanical strength.
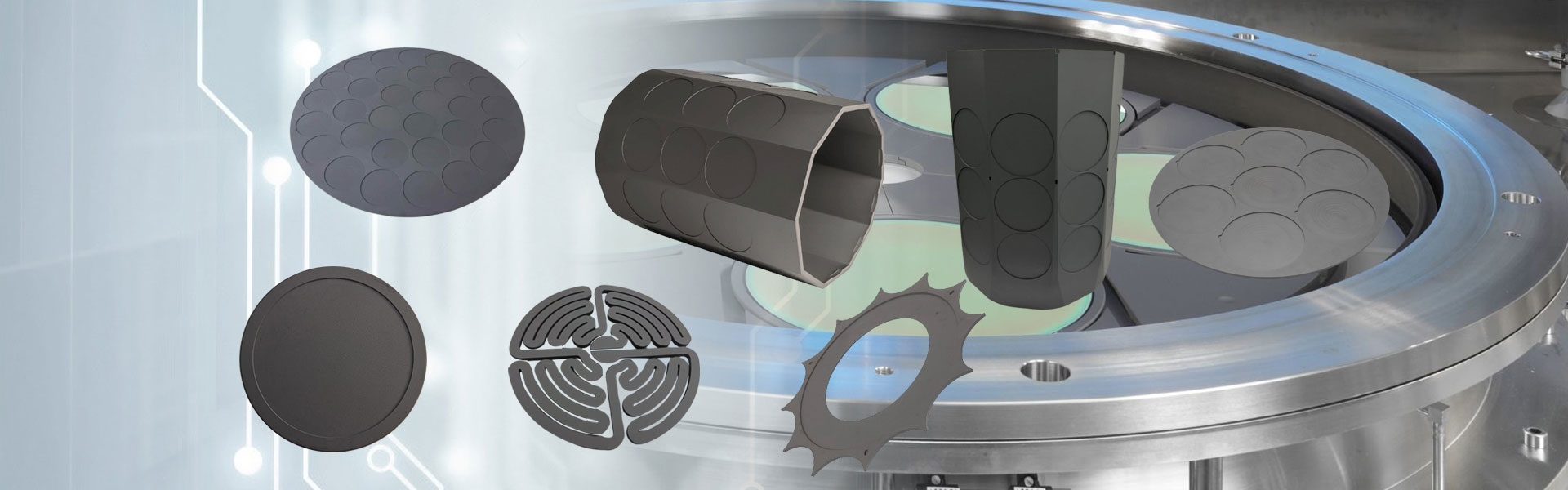
Isostatically pressed graphite is widely used in semiconductor manufacturing processes. It is used in graphite components for the hot zone of single crystal growth furnaces, such as crucibles, heaters, flow guides, and insulation covers; and in graphite components used in epitaxial processes.
- View as
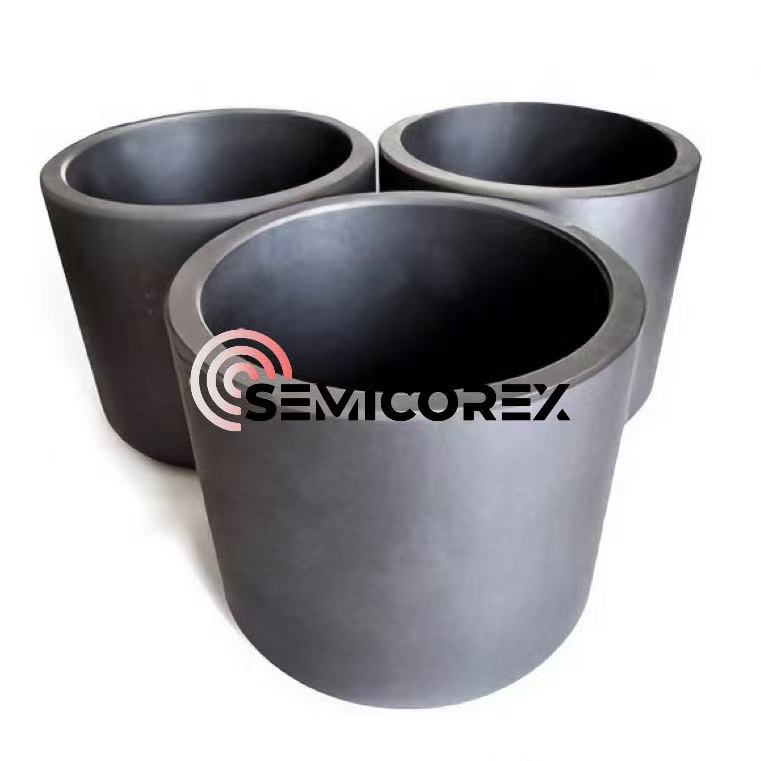
SiC 코팅 흑연 도가니
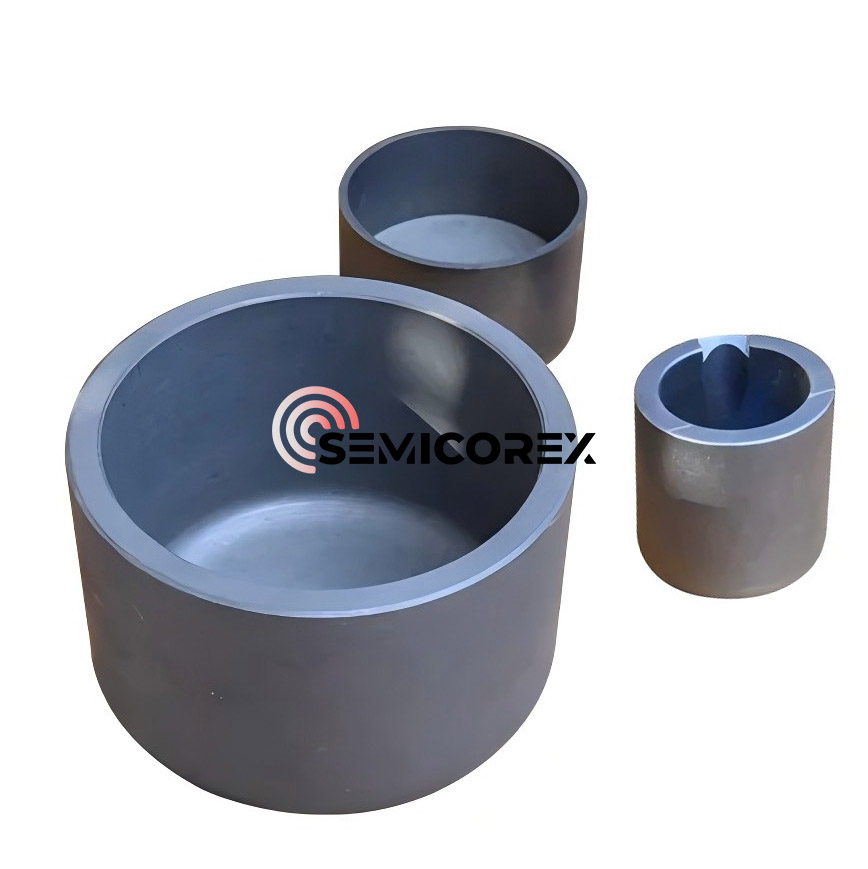
SiC 코팅 흑연 도가니는 탄화규소 코팅 흑연 소재를 정밀 가공한 필수 용기로, 뛰어난 내열성과 화학적 내식성을 제공합니다. 우수한 성능과 신뢰할 수 있는 품질을 갖춘 Semicorex의 SiC 코팅 흑연 도가니는 제어된 고품질 결정 생산을 달성하기 위한 최적의 솔루션입니다.
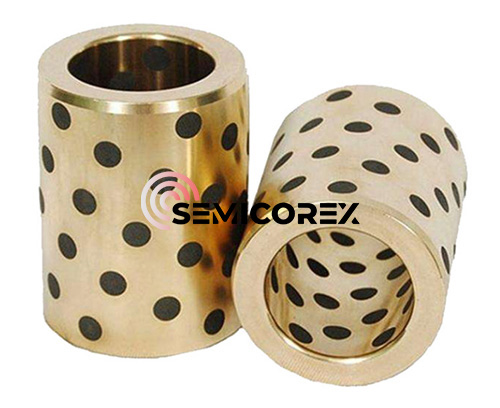
더 읽어보기문의 보내기탄소 흑연 베어링 및 부싱
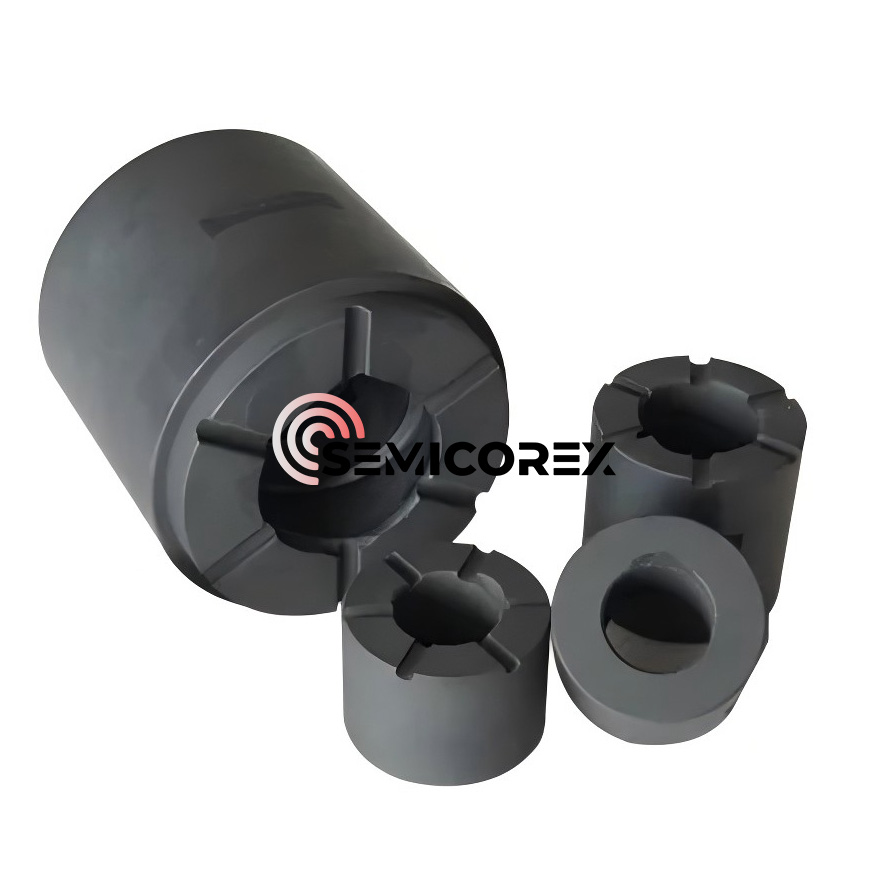
Semicorex 탄소 흑연 베어링 및 부싱은 기계 산업에서 널리 사용되는 고품질 탄소 흑연으로 만들어집니다. Semicorex는 고객의 요구 사항에 따라 검증된 제품을 제공합니다.*
더 읽어보기문의 보내기